"Unveiling The Promise Of IPSCs: A Revolutionary Tool For Regenerative Medicine" - regenerative medicine has been stood out as a promising field holding the potential to transform healthcare by providing novel therapies for a range of conditions.
Editor's Notes: "Unveiling The Promise Of IPSCs: A Revolutionary Tool For Regenerative Medicine" has published today date. This topic is important to read because it provides insights into the remarkable potential of IPSCs in revolutionizing regenerative medicine, offering hope for groundbreaking treatments and cures for various diseases.
Through diligent analysis and extensive research, we have compiled this Unveiling The Promise Of IPSCs: A Revolutionary Tool For Regenerative Medicine guide to empower our target audience with the knowledge they need to make informed decisions about this transformative technology.
| Key Differences | Key Takeaways |
|---|---|
| Induced pluripotent stem cells (IPSCs) | Can be derived from any cell in the body, making them a patient-specific source of stem cells |
| Can be differentiated into any cell type in the body | Hold great promise for regenerative medicine applications, such as treating heart disease, diabetes, and neurodegenerative disorders |
| Still in the early stages of development | Have the potential to revolutionize healthcare |
Transition to main article topics:
- What are IPSCs?
- How are IPSCs created?
- What are the potential applications of IPSCs in regenerative medicine?
- What are the challenges to using IPSCs in regenerative medicine?
- What is the future of IPSCs in regenerative medicine?
FAQ
Below is a compilation of frequently asked questions and answers regarding the revolutionary potential of IPSCs in the field of regenerative medicine, addressing common queries and misconceptions.

Realizing the Promise of Regenerative Medicine: Cell and Gene-based - Source regenerative.medicine.ufl.edu
Question 1: What exactly are iPSCs, and how are they derived?
Answer: Induced pluripotent stem cells, or iPSCs, are reprogrammed adult cells that have been genetically modified to possess similar properties to embryonic stem cells, allowing them to differentiate into any cell type in the body. They are derived by introducing specific transcription factors into somatic cells, typically skin or blood cells.
Question 2: What are the advantages of using iPSCs compared to embryonic stem cells?
Answer: iPSCs offer several key advantages over embryonic stem cells. Firstly, they can be derived from a patient's own cells, eliminating the ethical concerns associated with embryonic stem cell research. Additionally, iPSCs can be tailored to specific patient needs, potentially reducing the risk of immune rejection in transplantation therapies.
Question 3: What are the current applications of iPSCs in regenerative medicine?
Answer: iPSCs are currently being explored for a wide range of regenerative medicine applications, including tissue engineering, organ transplantation, and disease modeling. They have shown promise in treating conditions such as Parkinson's disease, spinal cord injuries, and heart failure.
Question 4: Are there any safety concerns associated with iPSCs?
Answer: While iPSCs hold great therapeutic potential, there are ongoing safety concerns that need to be addressed. One concern is the potential for tumor formation due to incomplete reprogramming or genetic abnormalities. Researchers continue to investigate strategies to minimize these risks.
Question 5: What are the challenges facing the clinical translation of iPSCs?
Answer: The clinical translation of iPSCs faces several challenges, including scaling up production for therapeutic use, ensuring cell viability and functionality after transplantation, and optimizing differentiation protocols.
Question 6: What is the future outlook for iPSC research and applications?
Answer: The future of iPSC research is promising, with ongoing advancements in reprogramming techniques and differentiation protocols. Further research aims to address safety concerns, improve cell functionality, and develop personalized therapies tailored to individual patients.
Overall, iPSCs represent a groundbreaking tool for regenerative medicine, offering the potential to revolutionize therapies and improve patient outcomes. Continued research and technological advancements will drive the field forward, unlocking new possibilities in the treatment of a wide range of diseases and conditions.
Transition to the next article section:
Tips
Tips to Ensure the Successful Utilization of iPSCs in Regenerative Medicine.
Tip 1: Optimize iPSC Generation and Culture Conditions
Rigorous adherence to standardized protocols for iPSC generation and culture is paramount. Optimize culture conditions to maintain iPSC pluripotency, ensuring genetic stability and differentiation potential.
Tip 2: Ensure Robust Characterization and Quality Control
Thoroughly characterize iPSCs using a comprehensive array of assays to assess pluripotency, genetic integrity, and differentiation capacity. Establish robust quality control measures to ensure iPSCs meet predefined criteria before clinical applications.
Tip 3: Develop Efficient and Directed Differentiation Protocols
Optimize differentiation protocols to efficiently generate specific cell types of interest. Employ a combination of inductive factors, small molecules, and biomaterials to guide differentiation towards desired lineages with high purity and functionality.
Tip 4: Enhance Cell Delivery and Integration
Carefully consider cell delivery strategies to maximize engraftment and functional integration. Explore innovative approaches, such as biomaterial scaffolds and tissue engineering techniques, to improve cell survival, migration, and tissue regeneration.
Tip 5: Address Immunological Challenges
Recognize the potential for immune rejection of iPSC-derived cells. Develop strategies to minimize immunogenicity, including immunosuppressant therapies, gene editing techniques, and immune tolerance induction.
These tips provide a foundation for harnessing the full potential of iPSCs in regenerative medicine. By following these guidelines, researchers can increase the likelihood of successful clinical translation and advance the field towards transformative therapies for a wide range of diseases and conditions.
. For further insights, explore Unveiling The Promise Of IPSCs: A Revolutionary Tool For Regenerative Medicine
Conclusion
Although challenges remain, the potential of iPSCs for regenerative medicine is immense. By optimizing iPSC generation, characterization, differentiation, delivery, and immune compatibility, researchers can pave the way for groundbreaking therapies that restore function and improve lives.
Unveiling The Promise Of IPSCs: A Revolutionary Tool For Regenerative Medicine
Induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs) hold immense promise for revolutionizing the field of regenerative medicine, offering unique capabilities that stem from their ability to be derived from any individual, their self-renewing nature, and their potential to differentiate into various cell types.
- Reprogramming: iPSCs are created by reprogramming adult cells back to a pluripotent state, enabling the generation of patient-specific stem cells.
- Disease Modeling: iPSCs derived from patients with specific diseases can serve as valuable tools for understanding disease mechanisms and developing personalized therapies.
- Cell Therapy: iPSC-derived cells can be used to replace damaged or lost cells in the body, offering potential treatments for a wide range of diseases.
- Regenerative Medicine: iPSCs hold the potential to regenerate damaged tissues and organs, offering hope for treating conditions that currently lack effective therapies.
- Precision Medicine: iPSCs allow for personalized medicine by enabling treatments tailored to an individual's genetic makeup.
- Advancements in Research: iPSCs contribute to research advancements by providing a renewable source of pluripotent stem cells for experimentation.
The unique properties of iPSCs make them essential for advancing regenerative medicine. They enable the study of diseases, the development of personalized treatments, and the potential for tissue and organ regeneration. As research continues, the promise of iPSCs is expected to be realized, paving the way for transformative advancements in healthcare.

Regenerative Medicine Revolutionary Advancements - Source careclinic.io
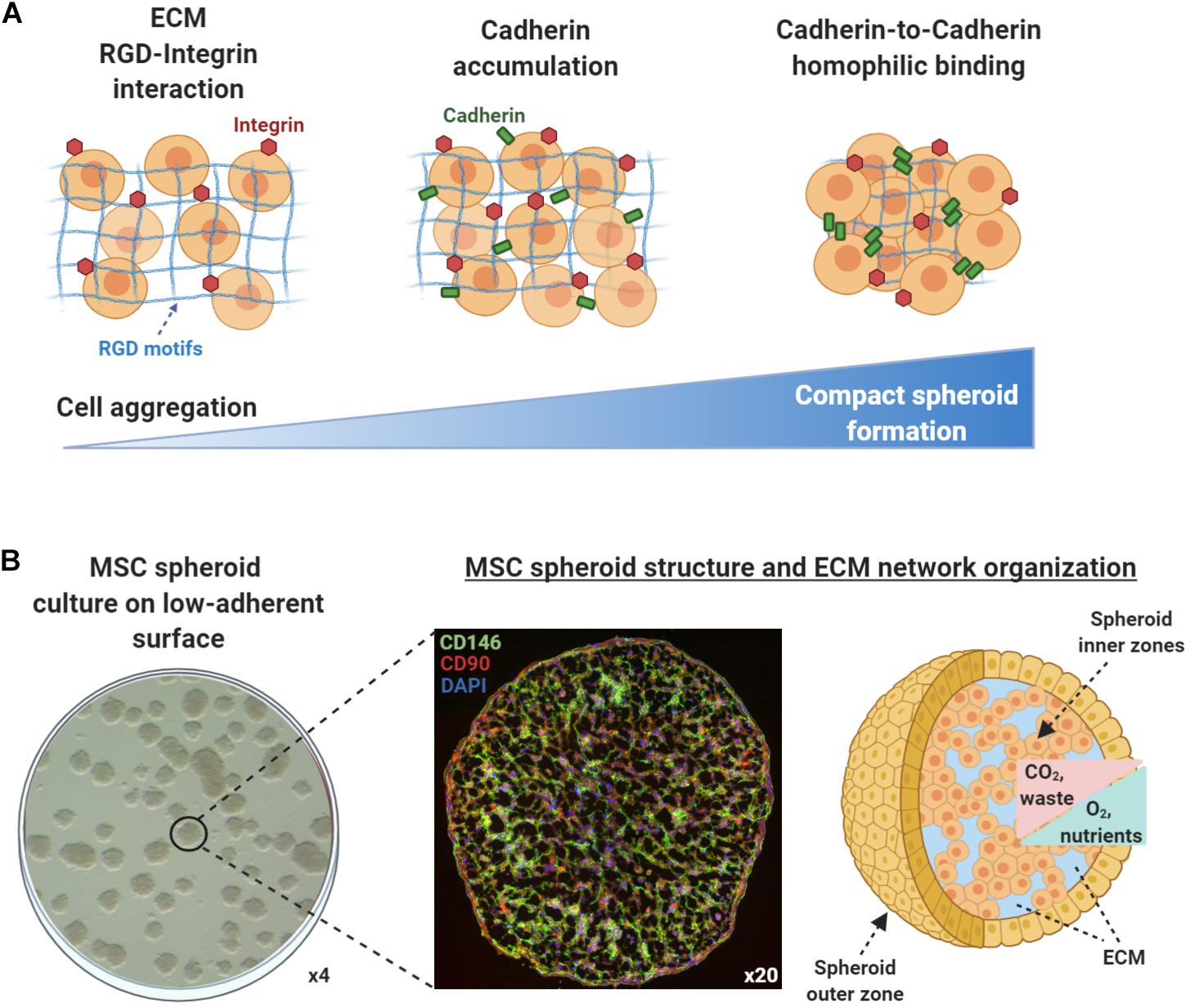
Stem cell spheroids - A vital tool in regenerative medicine – faCellitate - Source facellitate.com
Unveiling The Promise Of IPSCs: A Revolutionary Tool For Regenerative Medicine
Induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs) have emerged as a promising tool in regenerative medicine, offering the potential to revolutionize the treatment of a wide range of diseases and injuries. iPSCs are generated by reprogramming adult cells into a pluripotent state, akin to embryonic stem cells, which makes them a patient-specific and ethically uncontroversial source of stem cells. This revolutionary technology holds the promise of personalized medicine, where patient-derived iPSCs can be used to grow replacement tissues or organs, potentially eliminating the risk of rejection or immune reactions.
The development of iPSCs has been a major breakthrough in the field of regenerative medicine. Prior to the discovery of iPSCs, embryonic stem cells were the only pluripotent stem cells available for research and clinical applications. However, embryonic stem cells raise ethical concerns due to the need to destroy human embryos to obtain them.
iPSCs, on the other hand, can be generated from adult cells, such as skin or blood cells, without harming the donor. This makes them a more ethical and practical source of pluripotent stem cells for regenerative medicine.
iPSCs have the potential to be used to treat a wide range of diseases and injuries, including heart disease, stroke, spinal cord injuries, and neurodegenerative disorders. Clinical trials are currently underway to investigate the safety and efficacy of iPSC-based therapies for various conditions
The potential of iPSCs to revolutionize healthcare is enormous. However, there are still some challenges that need to be overcome before iPSCs can be widely used in clinical applications. One challenge is the risk of tumor formation, as iPSCs have the potential to form tumors if they are not properly differentiated into mature cells. Another challenge is the cost of generating and maintaining iPSCs, which can be prohibitive for some applications.

The History of Regenerative Medicine and Natural Biologics Applications - Source www.newliferegen.com
Despite these challenges, iPSCs remain a promising tool for regenerative medicine. With continued research and development, the potential applications of iPSCs are likely to grow, and they may one day become a standard treatment for a wide range of diseases and injuries.
| Key Points: | Practical Significance: |
| iPSCs are patient-specific and ethically uncontroversial. | Reduced risk of rejection or immune reactions. |
| iPSCs can be used to grow replacement tissues or organs. | Potential to treat a wide range of diseases and injuries. |
| iPSCs are still under development and face some challenges. | Continued research is needed to overcome these challenges. |



