What is a Supernova?
Supernovae are among the most fascinating and powerful events in the universe, marking the explosive end of stellar evolution.
Editor's Notes: Supernova: The Explosive End Of Stellar Evolution has just published today. It is an important topic related to the evolution of stars and the formation of heavy elements. We have analyzed and gathered information from various sources to provide you with this comprehensive guide.
Our guide will delve into the key differences or takeaways of supernovae, covering the different types, causes, and consequences of these spectacular cosmic explosions.
Key Differences: Types of Supernovae
There are two main types of supernovae:
FAQ
This section addresses frequently asked questions about supernovae, the explosive endings of stellar evolution.
Question 1: What triggers a supernova?
A supernova occurs when a massive star exhausts its nuclear fuel and collapses under its own gravity, leading to a catastrophic explosion that releases an enormous amount of energy.
Question 2: How often do supernovae occur?
Supernovae are relatively rare events, with an estimated occurrence rate of one per 50 to 100 years in a galaxy the size of the Milky Way.
Question 3: What are the different types of supernovae?
There are two main types of supernovae: Type Ia and Type II. Type Ia supernovae result from the explosion of a white dwarf star, while Type II supernovae originate from the collapse of a massive star.
Question 4: What are the observable effects of a supernova?
A supernova explosion produces a blinding flash of light, visible from across vast distances in space. It also releases a shock wave that can trigger the formation of new stars and leave behind a remnant object, such as a neutron star or a black hole.
Question 5: What is the role of supernovae in the evolution of galaxies?
Supernovae play a crucial role in the chemical enrichment of galaxies. They release heavy elements, such as iron and gold, into the interstellar medium, which are then incorporated into new generations of stars and planets.
Tips
Understanding the complex processes of stellar evolution can be enhanced by exploring additional resources. Consider delving into the depths of Supernova: The Explosive End Of Stellar Evolution to gain a comprehensive perspective on this fascinating astrophysical phenomenon.
Tip 1: Familiarize yourself with the Hertzsprung-Russell diagram to visualize the evolutionary paths of stars based on their luminosity and temperature.
Tip 2: Study the life cycle of stars, from their formation in interstellar clouds to their ultimate fate as white dwarfs, neutron stars, or black holes.
Tip 3: Investigate the types of supernovae, including Type Ia, Type Ib, and Type II, and their unique characteristics.
Tip 4: Explore the role of supernovae in the synthesis of heavy elements, contributing to the enrichment of the interstellar medium.
Tip 5: Examine the impact of supernova remnants on the surrounding environment, shaping interstellar clouds and triggering star formation.
To fully grasp the intricacies of stellar evolution and the significance of supernovae, delve into reputable scientific articles, books, and educational websites.
Supernova: The Explosive End Of Stellar Evolution
Supernovas, the colossal explosions marking the end of massive stars, are pivotal events in the cosmic dance. They unleash extraordinary energy, forge heavy elements, and shape the tapestry of galaxies. Delving into their explosive nature, we explore six key dimensions of this stellar cataclysm.
Supernovas are not mere stellar epitaphs; they are transformative cosmic events. They sculpt galaxies, create the chemical foundations for life, and illuminate the vastness of the universe. Their explosive brilliance serves as a testament to the dynamic and awe-inspiring nature of stellar evolution.
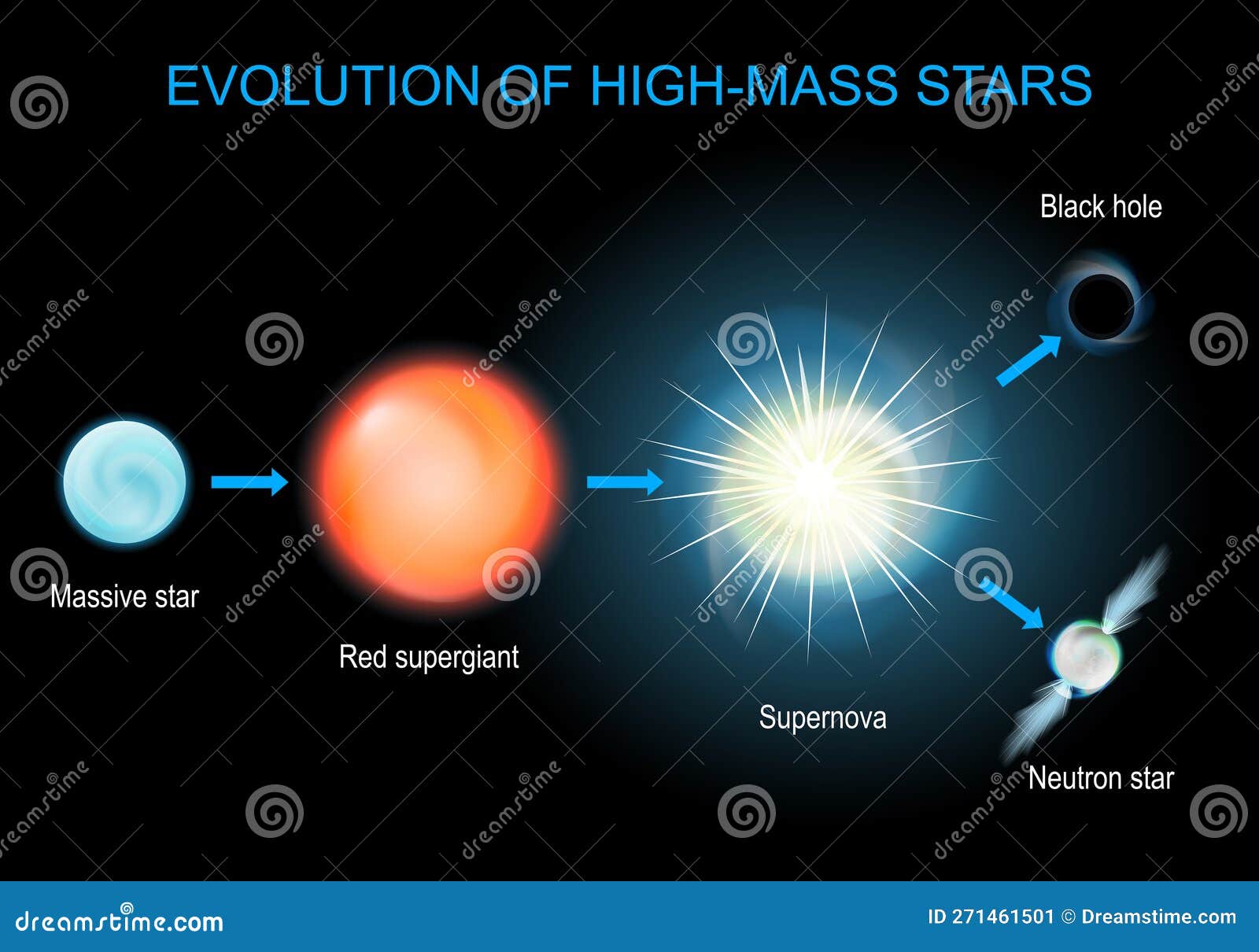
Evolution of High-mass Stars Stock Vector - Illustration of outer - Source www.dreamstime.com
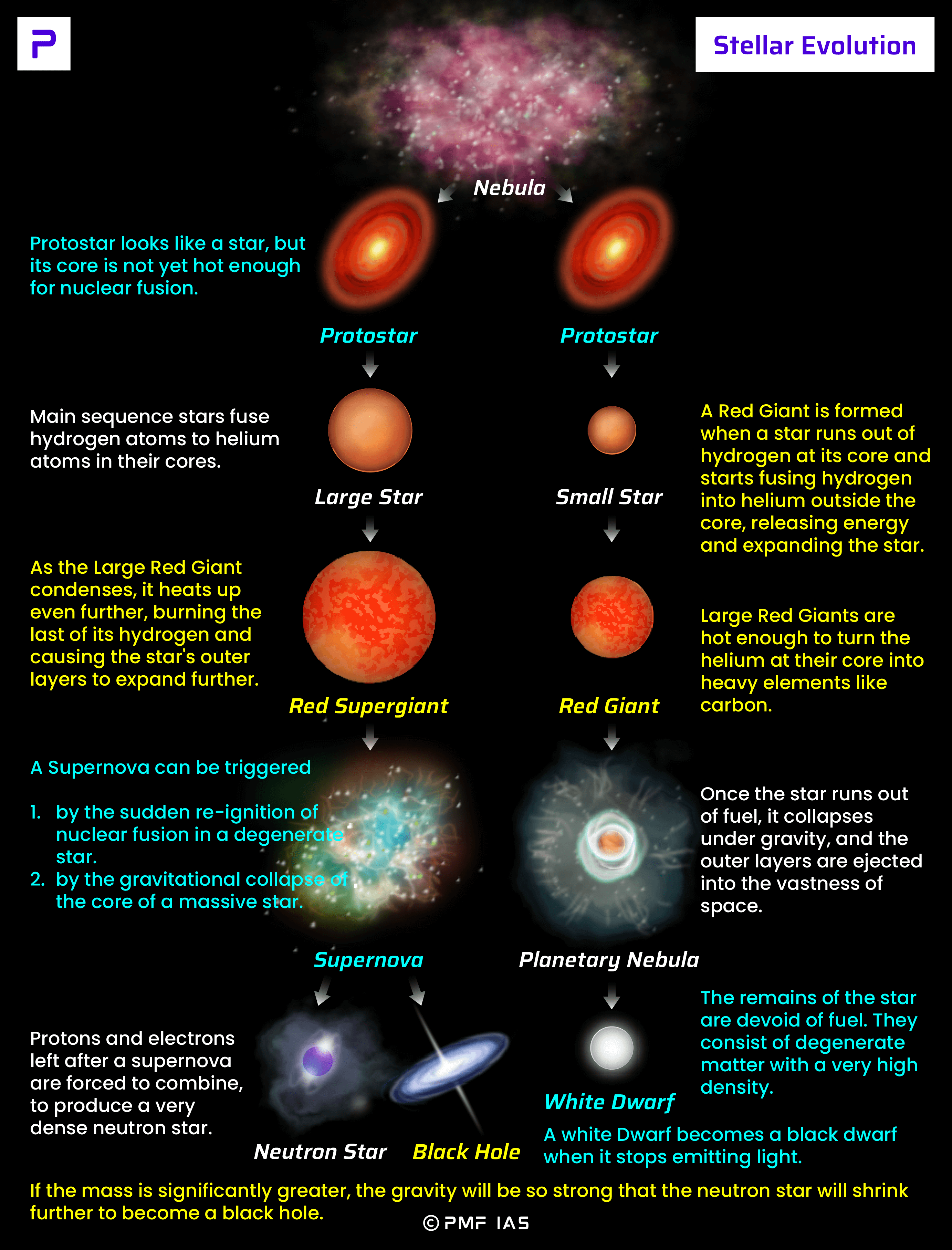
Astronomers Witness the Full Cycle of Stellar Evolution - Source chimniii.com
Supernova: The Explosive End Of Stellar Evolution
A supernova is a powerful explosion that occurs at the end of the life of a massive star. It is caused by the star's core collapsing under its own gravity, which then triggers a thermonuclear explosion that releases an enormous amount of energy. Supernovae are incredibly bright and can outshine entire galaxies, and they can also produce heavy elements that are essential for life. The study of supernovae is important for understanding the evolution of stars and the universe, and it has also led to the development of new technologies, such as medical imaging and nuclear power.

Evolution of a Supernova | NASA Jet Propulsion Laboratory (JPL) - Source www.jpl.nasa.gov
One of the most important aspects of supernovae is their role in the formation of heavy elements. When a massive star explodes as a supernova, it releases a large amount of energy that can fuse atoms together to form heavier elements. These heavy elements are then ejected into space, where they can be incorporated into new stars and planets. Supernovae are therefore responsible for the creation of all the elements heavier than iron, including the elements that are essential for life, such as carbon, nitrogen, and oxygen.
The study of supernovae has also led to the development of new technologies. For example, the study of supernovae has helped scientists to develop new medical imaging techniques that use radioactive isotopes to diagnose and treat diseases. Supernovae have also been used to study the expansion of the universe, which has led to the development of new theories about the origin and evolution of the universe.
Supernovae are a powerful and fascinating phenomenon that teaches us about the evolution of stars and the universe. They are also a source of new elements and new technologies. The study of supernovae is therefore an important field of research that has the potential to lead to new discoveries and new applications.
| Element | Atomic Number | Supernova Origin |
|---|---|---|
| Carbon | 6 | Yes |
| Nitrogen | 7 | Yes |
| Oxygen | 8 | Yes |
| Iron | 26 | No |
| Gold | 79 | Yes |
| Uranium | 92 | Yes |
Conclusion
Supernovae are a powerful and fascinating phenomenon that play an important role in the evolution of stars and the universe. They are also a source of new elements and new technologies. The study of supernovae is therefore an important field of research that has the potential to lead to new discoveries and new applications.
One of the most important challenges in the study of supernovae is the fact that they are so rare. Supernovae only occur once every few hundred years in a galaxy, so it is difficult to study them in detail. However, astronomers are now able to use telescopes to study supernovae in other galaxies, and they are also developing new techniques to study supernovae that are closer to Earth. These new techniques are helping astronomers to learn more about supernovae and their role in the universe.
The study of supernovae is also important for understanding the future of the universe. Supernovae are thought to be responsible for the formation of black holes, and they may also play a role in the expansion of the universe. By studying supernovae, astronomers can learn more about the future of the universe and its ultimate fate.



