Stagflation: An economic conundrum characterized by low economic growth, high inflation, and high unemployment, simultaneously. The term, coined by British politician Iain Macleod, combines 'stagnation' and 'inflation' aptly. It poses significant challenges for policymakers, as traditional tools to combat inflation may further worsen economic growth and unemployment. Understanding Stagflation and its implications is crucial for navigating such complex economic environments.
Editor's Notes: Stagflation: Understanding The Economic Conundrum And Its Implications have published today date, June 22nd, 2023. Stagflation is a critical topic that affects economies and individuals worldwide. Our team has analyzed and researched extensively to provide a comprehensive guide on Stagflation: Understanding The Economic Conundrum And Its Implications.
Our guide on Stagflation: Understanding The Economic Conundrum And Its Implications aims to provide readers with a deeper understanding of this complex economic phenomenon. We have compiled key information, insights, and implications to help businesses, policymakers, and individuals navigate the challenges posed by stagflation effectively. Join us as we delve into the intricacies of Stagflation: Understanding The Economic Conundrum And Its Implications.
Key Differences: Stagflation vs. Inflation, Recession, and Deflation
| Economic Condition | Economic Growth | Inflation | Unemployment |
|---|---|---|---|
| Stagflation | Low or Negative | High | High |
| Inflation | Positive | High | Variable |
| Recession | Negative | Variable | High |
| Deflation | Negative | Negative | High |
Main Article Topics
- Understanding Stagflation: Causes and Characteristics
- Stagflation: Economic and Societal Implications
- Policy Responses to Stagflation: Challenges and Considerations
- Stagflation in Historical Context: Lessons Learned and Risks
- Strategies for Businesses and Individuals during Stagflation
FAQ
This section addresses frequently asked questions (FAQs) about stagflation, its implications, and strategies for mitigating its impact.
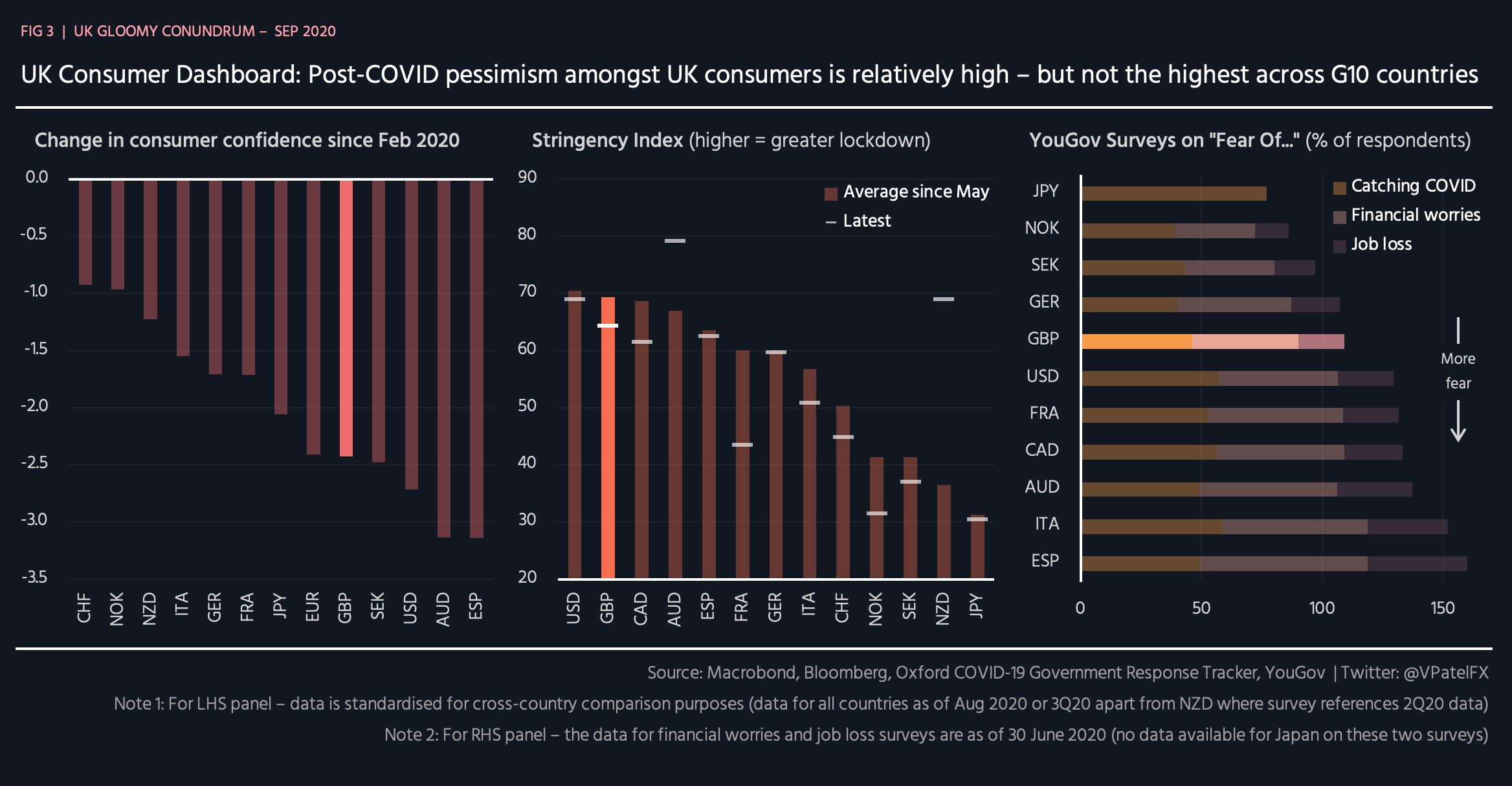
The U.K.'s Gloomy Economic Conundrum | Seeking Alpha - Source seekingalpha.com
Question 1: What is the root cause of stagflation?
Stagflation arises from a complex interplay of factors, including supply side disruptions, persistent inflation, and sluggish economic growth. External shocks (e.g., oil crises), structural shifts, and inadequate policy responses can all contribute to this economic conundrum.
Question 2: How does stagflation differ from other economic conditions?
Stagflation is distinguished by the simultaneous occurrence of high inflation and economic stagnation (low or negative growth). This situation creates a unique set of challenges for policymakers and businesses, as traditional tools for managing inflation or recession may prove ineffective.
Question 3: What are the economic implications of stagflation?
Stagflation can lead to reduced consumer spending, increased unemployment, and diminished investment. It can also erode purchasing power, weaken corporate profitability, and strain public finances. Stagflation's uncertainty and volatility can further undermine confidence and economic growth prospects.
Question 4: How can policymakers address stagflation?
Mitigating stagflation requires a delicate balancing act. Policies may include addressing supply-side constraints, implementing targeted monetary and fiscal measures, and promoting structural reforms to enhance economic flexibility and resilience. Cooperation between governments, businesses, and labor unions can also play a vital role.
Question 5: What strategies can businesses adopt to navigate stagflation?
Businesses can adopt various strategies to manage stagflation. These include cost optimization, supply chain diversification, product innovation, and exploring new markets. Maintaining strong cash flow and financial flexibility is crucial. Collaboration with government and industry partners can also provide support during challenging economic times.
Question 6: What lessons can be learned from historical episodes of stagflation?
Historical episodes of stagflation offer valuable lessons. Understanding the root causes, policy responses, and long-term impacts of past stagflationary periods can help policymakers and businesses better prepare for and mitigate the effects of future occurrences.
In conclusion, stagflation is a complex economic phenomenon with significant implications for economies and businesses. A comprehensive understanding of its causes, effects, and potential solutions is essential for navigating this challenging economic landscape.
Transitioning to the next article section: This knowledge can empower stakeholders to make informed decisions, adapt strategies, and mitigate the risks associated with stagflation.
Tips
Tips to address the economic conundrum of stagflation, a combination of stagnant economic growth and high inflation, which can be challenging to manage.
Tip 1: Implement Monetary Policy Tightening
Central banks can raise interest rates to reduce money supply and curb inflation. However, this may also slow down economic growth.
Tip 2: Pursue Fiscal Restraint
Governments can reduce spending and raise taxes to lower demand-side inflation. However, this may further suppress economic growth.
Tip 3: Address Supply-Side Issues
Identify and remove obstacles in production and distribution channels to increase output and reduce inflationary pressures.
Tip 4: Promote Wage and Price Controls
In exceptional circumstances, governments can temporarily impose measures to control wage increases and prices to curb inflation. However, this requires careful implementation and consideration of long-term consequences.
Tip 5: Encourage Long-Term Investment
Foster policies that support business investment and innovation to enhance productivity and increase potential output.
Summary: Stagflation presents a complex challenge. By carefully balancing these tips, policymakers can strive to address inflation while mitigating the negative effects on economic growth.
For further insights into the complexities of stagflation, refer to this comprehensive article: Stagflation: Understanding The Economic Conundrum And Its Implications
Stagflation: Understanding The Economic Conundrum And Its Implications
Stagflation, a perplexing economic phenomenon, manifests when an economy experiences the seemingly paradoxical combination of high inflation, slow economic growth, and high unemployment. This intricate conundrum poses significant challenges for policymakers and has substantial implications for businesses, consumers, and economies.

The TikTok Conundrum: Elon Musk's Potential Acquisition and Its - Source ilovetesla.com
- Origins: Often rooted in supply shocks and monetary expansion.
- Causes: Inflationary pressures from rising costs and stagnant aggregate demand.
- Consequences: Reduced purchasing power, hindered investment, and job losses.
- Policy Responses: Difficult trade-offs between combating inflation and supporting growth.
- Historical Examples: 1970s oil crisis and 2011 Arab Spring.
- Contemporary Implications: Potential impacts on economic recovery post-COVID-19.
Stagflation's complex dynamics demand a thorough understanding of its origins, causes, and consequences. It requires innovative policy interventions and highlights the importance of economic resilience and adaptability in the face of unforeseen economic challenges.
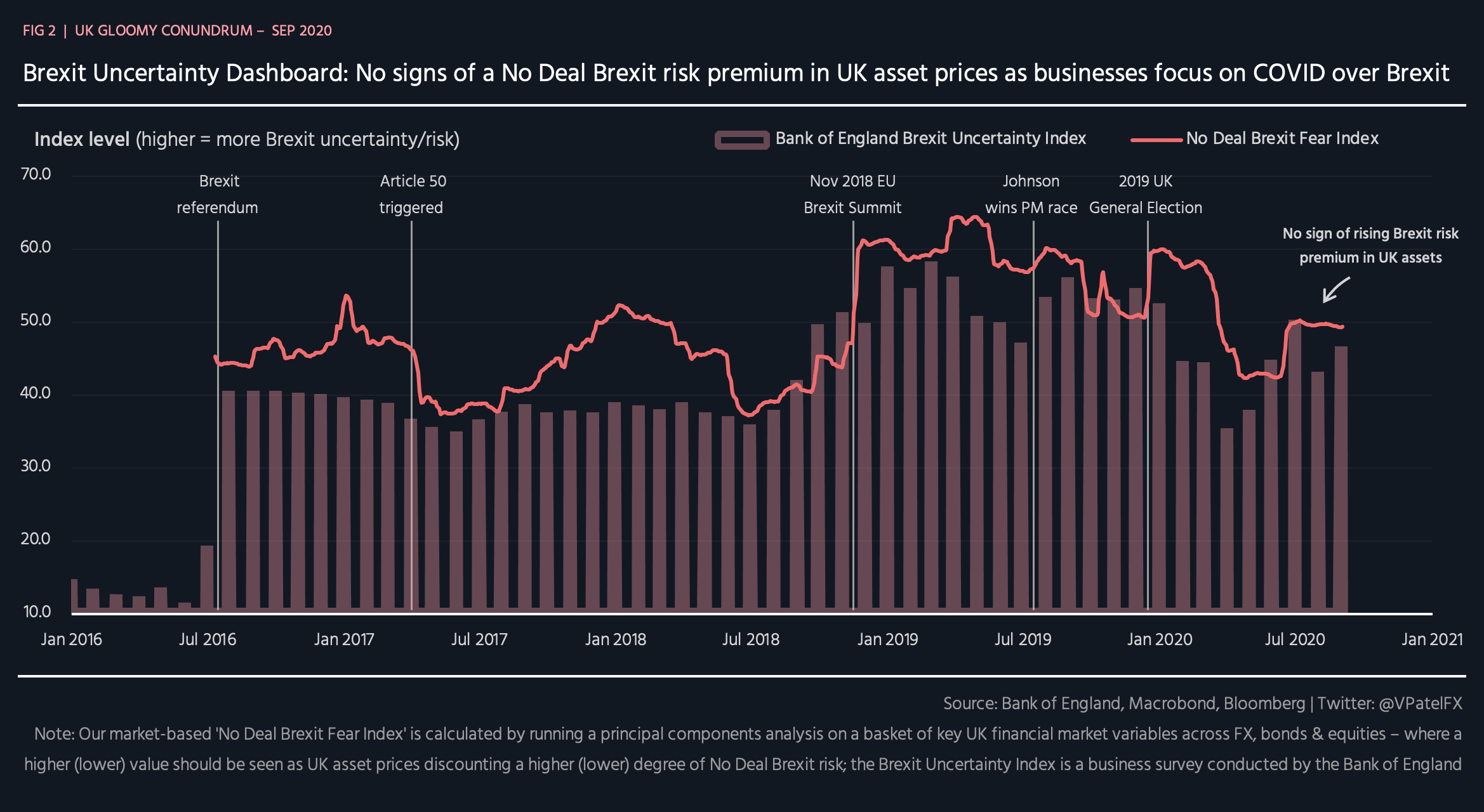
The U.K.'s Gloomy Economic Conundrum | Seeking Alpha - Source seekingalpha.com
Stagflation: Understanding The Economic Conundrum And Its Implications
Stagflation, characterized by high inflation, slow economic growth, and high unemployment, represents a perplexing economic challenge. It poses a double-edged sword, with traditional policy tools seemingly ineffective. Understanding the connection between its causes and effects is crucial for effective policy responses.
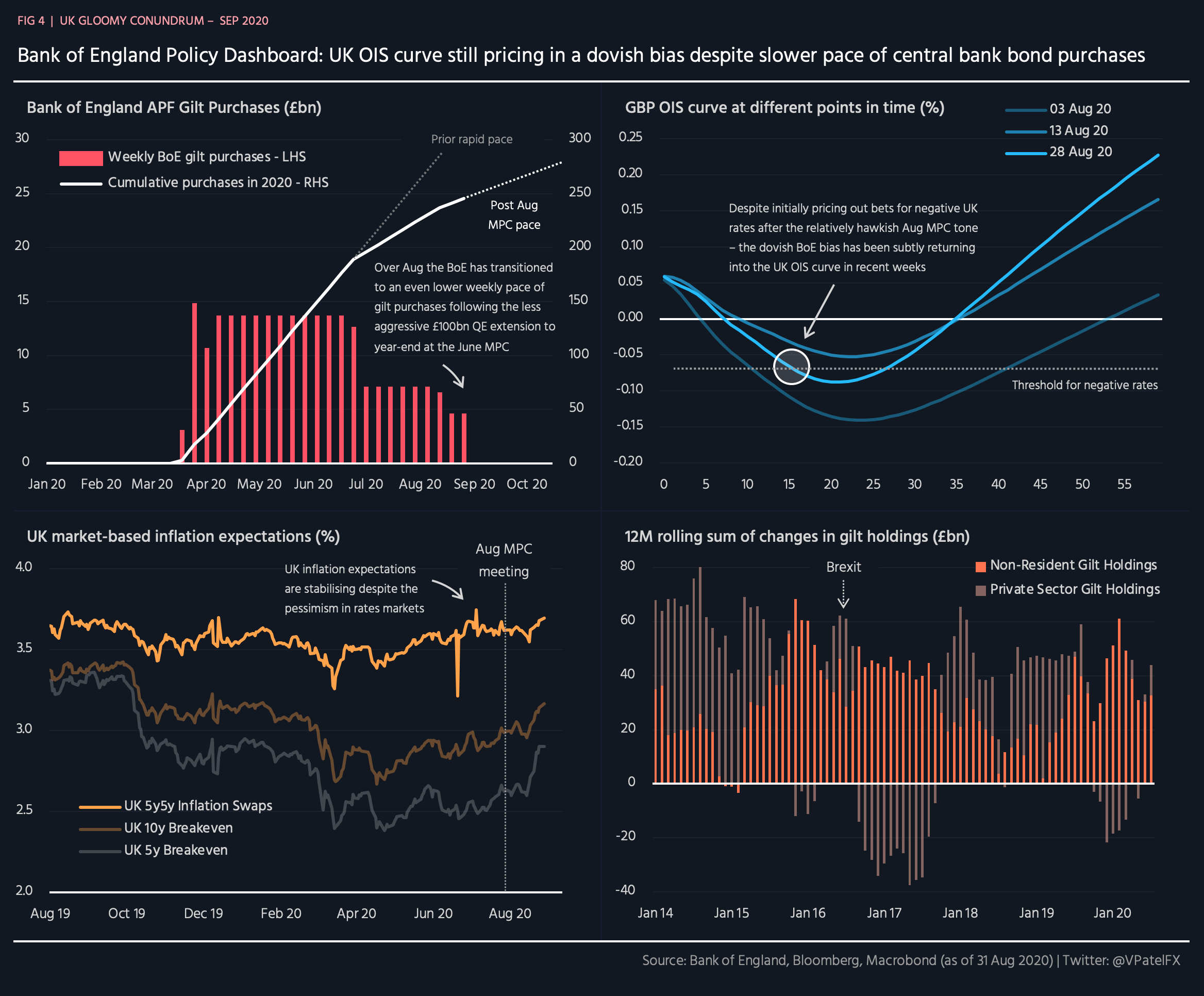
The U.K.'s Gloomy Economic Conundrum | Seeking Alpha - Source seekingalpha.com
Key to understanding stagflation is recognizing the interplay between supply and demand factors. Cost-push inflation, triggered by supply-side shocks like oil crises or supply chain disruptions, can elevate costs for businesses and consumers. Simultaneously, demand-side factors, such as excessive government spending or rapid credit growth, can fuel inflation by outpacing supply.
Addressing stagflation requires a nuanced approach, recognizing the unique dynamics at play. Monetary policies aimed at curbing inflation may inadvertently exacerbate unemployment. Fiscal policies intended to stimulate growth could further stoke inflation. The complexity of stagflation demands multifaceted solutions, balancing short-term measures with long-term structural reforms.
Stagflation poses significant risks to economic stability and societal well-being. Persistent high inflation erodes purchasing power, while high unemployment undermines livelihoods and social cohesion. Understanding the connection between stagflation's causes and effects equips policymakers and economists with the knowledge necessary to navigate this economic labyrinth.
Conclusion
Stagflation presents a formidable economic challenge, demanding a deep understanding of its causes and effects. Addressing it requires a delicate balance of policies, considering both supply-side and demand-side factors. By acknowledging the complexities of stagflation, policymakers can develop tailored solutions that mitigate its adverse consequences and foster sustainable economic growth.
Stagflation remains a subject of ongoing study and debate, as economists seek to refine their understanding of this multifaceted phenomenon. The insights gained contribute not only to managing stagflationary episodes but also to promoting economic stability and resilience over the long term.



